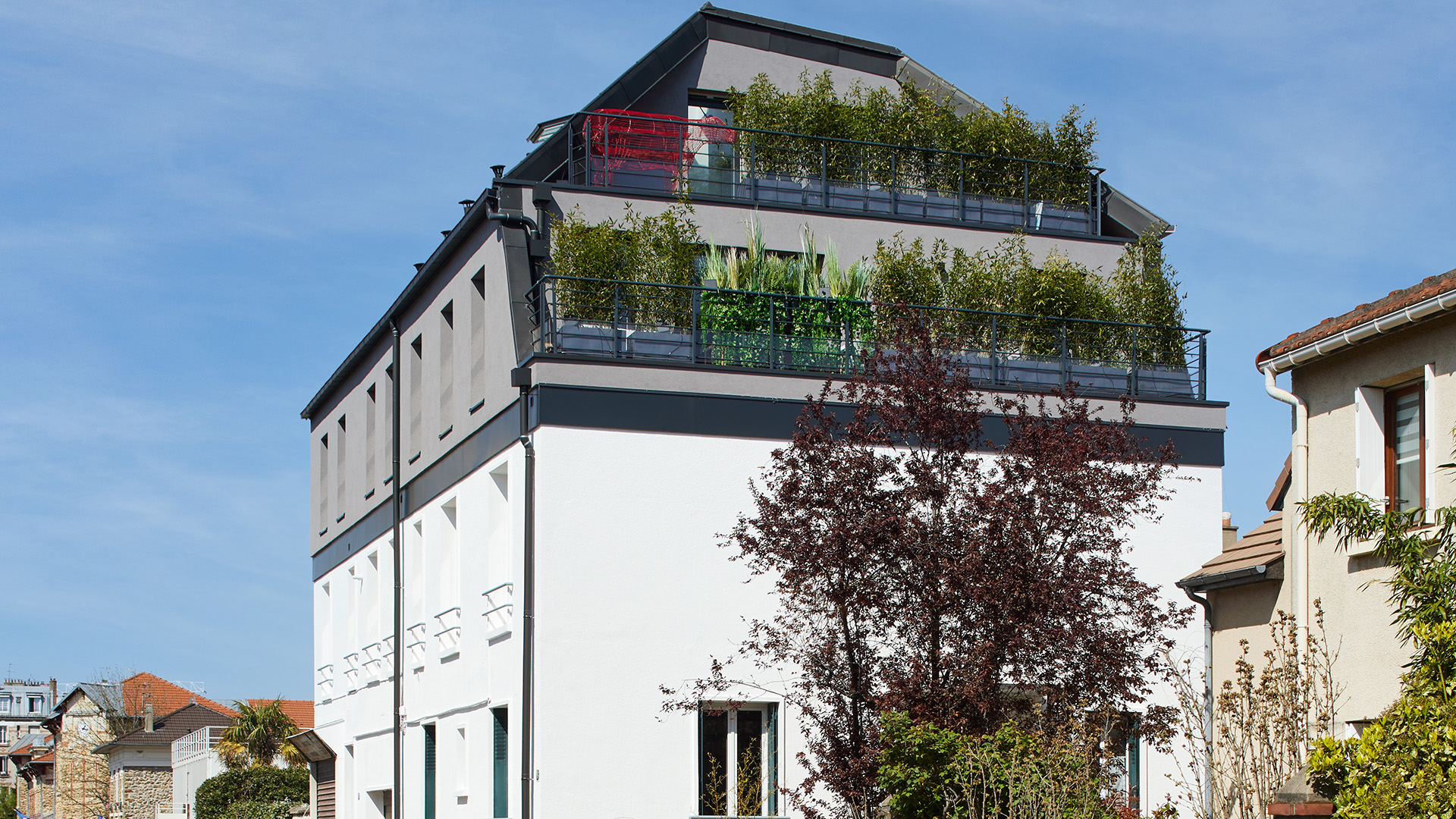
Type of building: Roof extension
Year of construction: 1900
Year of renovation: 2021
Location: Malakoff, France
Built-up area: 288m2
Project lead: UPFACTOR
Extending upwards
This raise-the-roof project added two new apartments on top of an existing building. To reduce environmental impact, the roof extension project used lightweight bio-based construction materials, including timber. Inside the project made use of passive cooling through ventilation and shading of roof windows, as well as insulation. The air quality was improved through the use of non-toxic materials and regular ventilation.
The result is a perfect space solution for densely populated areas. Furthermore, using off-site construction meant minimal disruption to existing inhabitants of the building.
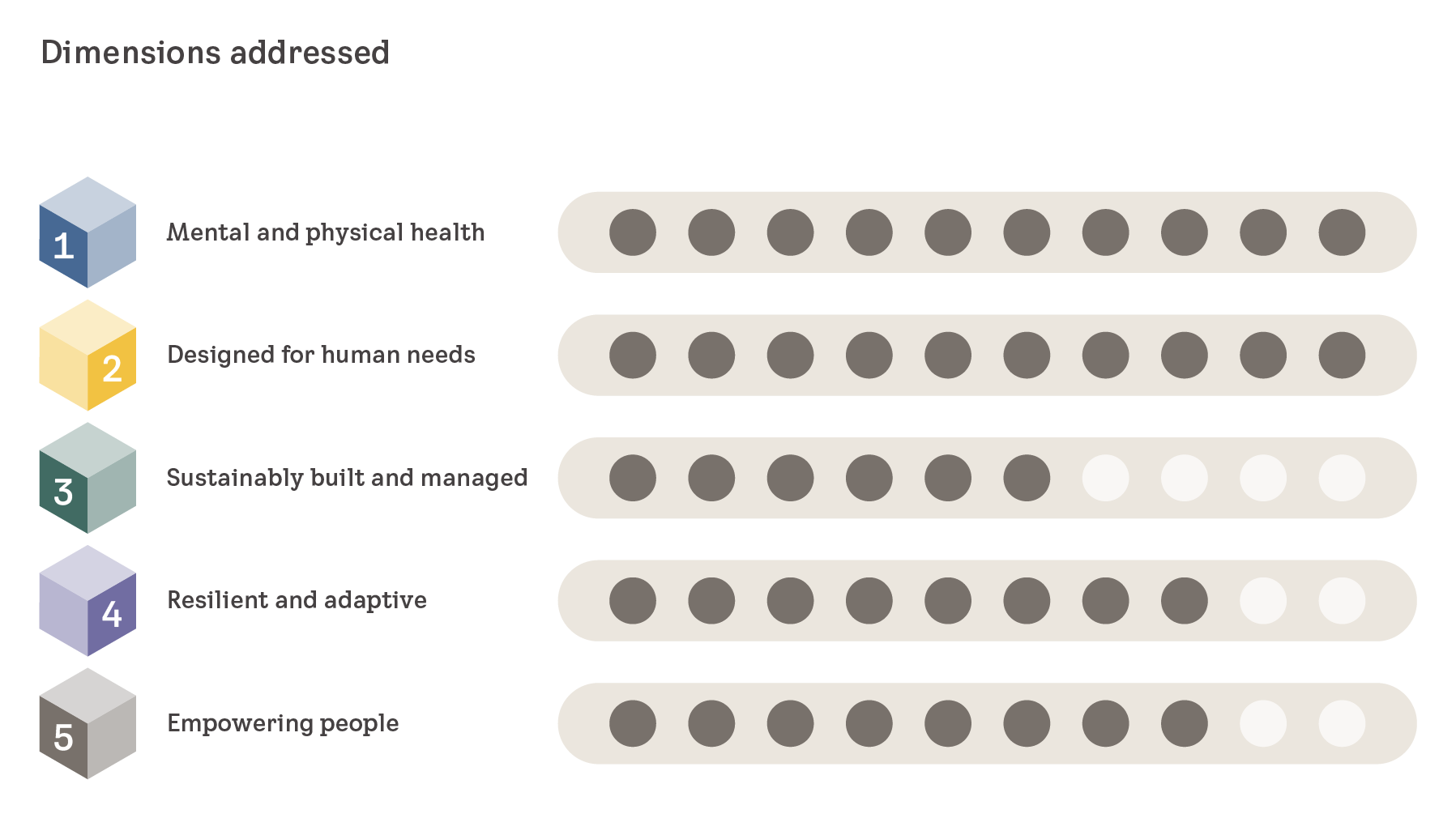
Dimensions
In order to comprehensively assess the health of the building in this case study, various dimensions were evaluated, each measured through specific indicators relevant to their respective domains. The following figure presents the ratings for each dimension, providing a visual summary of the building's overall health status.
Data insights for France
Europe’s climate is likely to become more unpredictable, both in terms of winter and summer temperatures. Monitoring the thermal comfort in buildings is therefore important for building health.
This case analysed data for the indicator Thermal comfort from the dimension Improving mental and physical health. It used two data sets representing winter and summer: the Inability to keep home warm and the Cooling Degree Days (the need to cool on hot days).
Affordability
EU data tracking the ability of people to keep their homes sufficiently warm and cool when needed since 2015 shows that we have experienced more cooling degree days in recent years. Furthermore, the ability to keep homes warm is getting worse, especially in France. Healthy building projects such as the raise-the-roof project in France can help people adapt to changes in temperatures.


